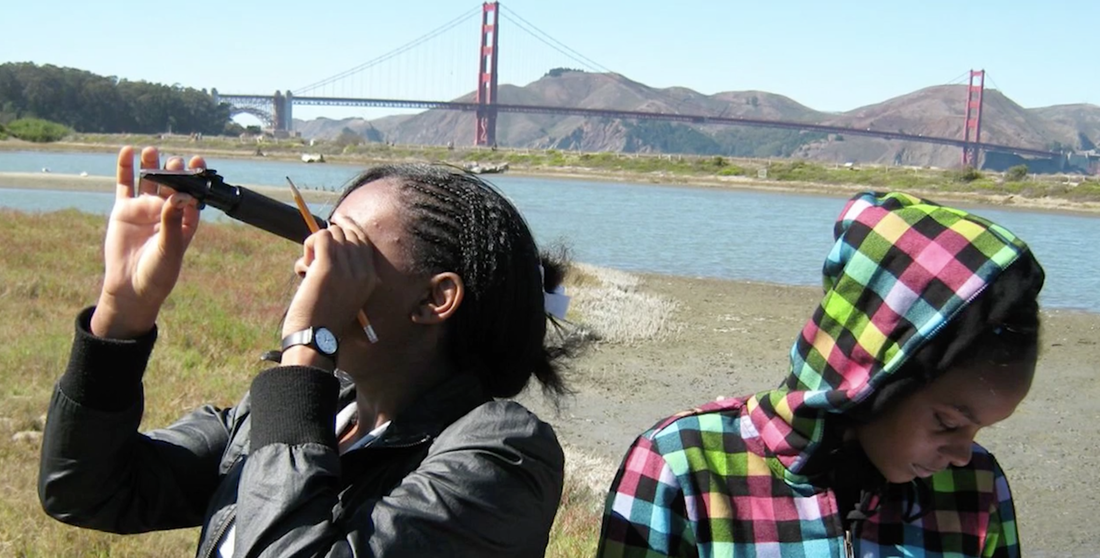
ABOUT THE LEARNING IN AFTERSCHOOL & SUMMER (LIAS) PROJECT
The Learning in Afterschool & Summer project is working to focus discussions within the afterschool
movement on what we know about children and their learning.
What this project tries to do is focus not on what young people should learn, rather focus on the how- program approaches that promote learning. You will notice that the exemplar afterschool programs - the ones that are the darlings of the afterschool movement - are all exceptional in how they promote young people’s excitement in learning. The same is true of those exceptional educators who are named as teachers of the year in local, state, and national ceremonies. What we hear most about these acclaimed classroom teachers are their abilities to motivate and excite young people in learning. But somehow we bypass the principles that they apply in practice. This project aims to focus our attention and practice on a few learning principles.
1. Learning that is Active
Learning and memory recall of new knowledge is strengthened through different exposures – seeing, hearing, touching, and doing. Afterschool learning should be the result of activities that involve young people in “doing” – activities that allow them to be physically active, stimulate their innate curiosity, and that are hands-on and project-based. ( CA Quality Standards #2, 3, & 5)
2. Learning that is Collaborative
Afterschool and summer programs should help young people build team skills that include listening to others, supporting group learning goals, and resolving differences and conflicts.
Collaborative learning happens when learners engage in a common task where each individual depends on and is accountable to each other. (CA Quality Standards #1, 2, 3, & 8)
3. Learning that is Meaningful
Learning is meaningful when youth have some ownership over the learning topic, the means to assess their own progress, and when the learning is relevant to their own interests, experiences, and the real world in which they live. Community and cultural relevance is important to all youth. (CA Quality Standards #2, 3, & 4)
4. Learning that Supports Mastery
If young people are to learn the importance and joy of mastery, they need the opportunity to learn and practice a full sequence of skills that will allow them to become “really good at something.” Afterschool and summer activities should be explicitly sequenced and designed to promote the layering of new skills. (CA Quality Standard #3)
5. Learning that Expands Horizons
Afterschool and summer programs should provide learning opportunities that take youth beyond their current experience and expand their horizons. They should go beyond the walls of their facilities to increase young people’s knowledge of their surrounding neighborhood and the larger global community. (CA Quality Standards #2 & 3)
movement on what we know about children and their learning.
What this project tries to do is focus not on what young people should learn, rather focus on the how- program approaches that promote learning. You will notice that the exemplar afterschool programs - the ones that are the darlings of the afterschool movement - are all exceptional in how they promote young people’s excitement in learning. The same is true of those exceptional educators who are named as teachers of the year in local, state, and national ceremonies. What we hear most about these acclaimed classroom teachers are their abilities to motivate and excite young people in learning. But somehow we bypass the principles that they apply in practice. This project aims to focus our attention and practice on a few learning principles.
1. Learning that is Active
Learning and memory recall of new knowledge is strengthened through different exposures – seeing, hearing, touching, and doing. Afterschool learning should be the result of activities that involve young people in “doing” – activities that allow them to be physically active, stimulate their innate curiosity, and that are hands-on and project-based. ( CA Quality Standards #2, 3, & 5)
2. Learning that is Collaborative
Afterschool and summer programs should help young people build team skills that include listening to others, supporting group learning goals, and resolving differences and conflicts.
Collaborative learning happens when learners engage in a common task where each individual depends on and is accountable to each other. (CA Quality Standards #1, 2, 3, & 8)
3. Learning that is Meaningful
Learning is meaningful when youth have some ownership over the learning topic, the means to assess their own progress, and when the learning is relevant to their own interests, experiences, and the real world in which they live. Community and cultural relevance is important to all youth. (CA Quality Standards #2, 3, & 4)
4. Learning that Supports Mastery
If young people are to learn the importance and joy of mastery, they need the opportunity to learn and practice a full sequence of skills that will allow them to become “really good at something.” Afterschool and summer activities should be explicitly sequenced and designed to promote the layering of new skills. (CA Quality Standard #3)
5. Learning that Expands Horizons
Afterschool and summer programs should provide learning opportunities that take youth beyond their current experience and expand their horizons. They should go beyond the walls of their facilities to increase young people’s knowledge of their surrounding neighborhood and the larger global community. (CA Quality Standards #2 & 3)
Our Other Projects
|
Temescal Associates is dedicated to building the capacity of leaders and organizations in education and youth development who are serious about improving the lives of young people.
|
Dedicated to providing those who are interested in improving youth outcomes with thought-provoking, educational opportunities
|
Expanded Learning 360°/365
Resources and Services to Promote Character Building and Social Emotional Learning in Youth Programs |
Curricula, materials, and additional resources to promote learning and healthy development in youth programs
|